

Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a forward-thinking environmental policy that places the responsibility for plastic waste management squarely on the shoulders of producers.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a forward-thinking environmental policy that places the responsibility for plastic waste management squarely on the shoulders of producers. As plastic pollution continues to burden ecosystems and communities, EPR ensures that companies introducing plastic packaging into the market are also responsible for its collection, recycling, and safe disposal. Introduced under the Plastic Waste Management (PWM) Rules,2016—and further reinforced in amendments—EPR is central to India’s efforts to reduce plastic pollution, encourage sustainable packaging, and shift waste management duties from public systems to private producers.
It promotes a circular economy by encouraging eco-friendly product design, reducing dependency on virgin plastics, and fostering collaboration between the public and private sectors.
Today, EPR is not just about compliance—it’s a business necessity and a mark of environmental leadership
Under Rule 9 of the Plastic Waste Management (PWM) Rules notified in 2016, EPR Registration is mandatory for all Producers, Importers, Brand Owners (PIBOs), and Plastic Waste Processors involved in plastic packaging in India.
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has launched a centralized EPR portal to simplify and standardize the registration process nationwide.
To register, businesses must compile operational and compliance-related documentation, submit an online application through the EPR portal, and pay the required registration fee. Depending on the scope of operations—single or multi-state—the application is reviewed by either the State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) or the CPCB.
A valid EPR Registration Certificate authorizes an entity to handle plastic waste responsibly. Non-compliance can lead to penalties, fines, or suspension of business operations. By registering under EPR, companies ensure they meet legal obligations while contributing meaningfully to environmental sustainability.
Registration under the EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) for Plastic Waste Management is a key regulation and sustainability instrument for contemporary businesses. What are the EPR registration benefits for PWM ?
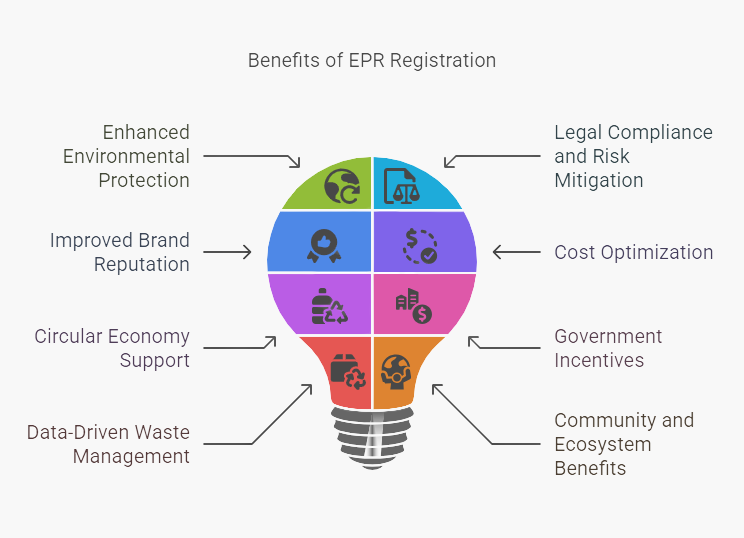
Better Environmental Protection: EPR registration holds manufacturers, importers,and brand owners responsible for the full lifecycle of their plastic products, from manufacture to post-consumer disposal. This accountability results in less plastic waste pollution, reduced landfill use, and fewer environmental hazards from unmanaged plastic waste. Through responsible product design and promoting the use of recyclable material, EPR supports a cleaner, healthier environment and helps conserve natural resources.
Compliance and Risk Management:EPR registration is a legal mandate for organizations that manufacture or deal with plastic products – in various geographies such as India – ensuring they meet environmental requirements. Compliance protects businesses from hefty fines, penalties, and even operational halts due to non-compliance. It ensures full legal alignment in plastic waste management and enables companies to operate with confidence.
Enhancement in Brand Visibility and Market Differentiation:Companies with EPR certification are recognized as environmentally responsible and sustainable, boosting brand value and consumer trust. Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability sets your brand apart in a competitive market, attracting eco-conscious customers and partners.
Cost Saving and Resource Efficiency:EPR motivates producers to adopt efficient waste management strategies, minimizing overall waste management costs through optimized collection, recycling, and disposal. Designing products with recyclability and resource conservation in mind offers long-term savings on materials and energy.
Championing Circular Economy Efforts:EPR registration is a key enabler for the circular economy—encouraging reuse and recycling of plastics. It reduces dependency on virgin materials and helps close the plastic waste loop, supporting sustainable business models. Businesses are encouraged to innovate in packaging and product design with recycling and reusability embedded in operations.
Availability of Government Incentives and Supports:Governments often provide incentives, subsidies, or preferential treatment to EPR-compliant businesses, helping to reduce costs and increase profitability.
Data-Led Approach to Waste Management with Built-in Mechanism for Improvement:EPR registration requires businesses to maintain detailed records of plastic use, waste generation, and recycling performance. This supports informed decision-making and continuous improvement in waste management.
Community and Ecosystem Benefits:Reducing plastic pollution and supporting recycling systems under EPR contributes to healthier communities, cleaner environments, and protection of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Summary:
EPR plastic registration is not just a regulatory step—it’s a strategic investment in sustainability, compliance, brand equity, cost efficiency, and green business practices. Companies embracing EPR are better prepared for long-term success, regulatory confidence, and public trust in today’s environmentally-conscious marketplace.
EPR is applicable to the following categories of plastic packaging:
Category I: Rigid Plastic Packaging
This includes any type of plastic packaging which is rigid and does not easily change shape under pressure. These are popular because they offer durability and protection.
Common Examples:
Key Points:
Category II: Flexible Plastic Packaging
Flexible plastic packaging can easily bend, fold, or twist. This includes single-layer and multi-layer flexible plastics.
Common Examples:
Key Points:
Category III: Multi-layered Plastic Packaging
These are materials that combine at least one plastic layer with others (like paper, aluminium, or various polymers), improving barrier properties and extending shelf life.
Common Examples:
Key Points:
Category IV: Compostable Plastic Packaging
Made from compostable materials, these break down into natural elements under composting conditions without leaving toxic residue.
Common Examples:
Key Points:
According to the Plastic Waste Management Rules, all Producers, Importers, and Brand Owners (PIBOs) must put a robust plastic waste collection system in place within six months of the rule’s notification. This system must align with EPR norms and should be executed in coordination with State Urban Development Authorities, local bodies, or through independent distribution networks.
Every producer is required to maintain records of all suppliers of plastic used as raw material—whether for carry bags, packaging, sheets, or multi-layered plastics. This documentation ensures product traceability and compliance with regulations.
The following entities must obtain an EPR registration certificate through the centralized EPR portal developed by CPCB:
Registering on the CPCB EPR portal is a mandatory step toward legal compliance and responsible plastic packaging waste management. This system is essential in promoting a cleaner environment and supporting a circular economy.
he following documents for the pre-requisite of registration requirement in the Plastic Waste Management Rules are to be furnished by Producers, Importers, Brand Owners (PIBOs) and Plastic Waste Processors (PWPs) on the EPR portal of CPCB, who require the registration certificate under the EPR rule: Documentary requirement against pre-requisite of registration requirement under Plastic Waste Management Rule.
These papers would help ensure transparency, traceability, and compliance under the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) regime standardised by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) for plastic waste management in India.
Producers, Importers, Brand Owners (PIBOs), and Plastic Waste Processors (PWPs) are required to obtain EPR registration under the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) rules via the centralized CPCB EPR portal in accordance with the Plastic Waste Management Rules.
Detailed EPR Registration Process:
1. Document Preparation: Before beginning the application, gather all necessary documents in PDF, JPG, or PNG format. These include proof of business identity, production details, and EPR compliance documentation.
2. User Registration on EPR Portal: Applicants must first complete a self-registration on the official CPCB EPR portal. This step generates login credentials and grants access to the application dashboard.
3. Filling the EPR Application Form: Once registered, Producers, Importers, or Brand Owners must log in and fill out their respective EPR application forms. These forms include section-wise details and require uploading supporting documents related to plastic waste management obligations.
4. Online Fee Payment: Applicants must pay the prescribed EPR registration fee through the portal’s integrated payment gateway. The application will only be considered valid once the payment is made.
5. Application Review by CPCB/SPCB: For entities operating in one or two states: Applications are forwarded to the relevant State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) or Pollution Control Committees (PCCs) for review.
For multi-state operations: Applications are reviewed directly by CPCB officials.
6. Approval & EPR Certificate Issuance: Upon successful verification, the relevant authority (CPCB/SPCB/PCC) issues a digitally signed EPR Registration Certificate within 15 working days. Applications that are incomplete or contain false information will be rejected. Approved certificates can be downloaded from the portal.
A. EPR Application Fees for PIBOs (Producers, Importers, and Brand Owners)
| Sr.No |
Plastic Waste Generation (TPA) |
EPR Registration Fee (INR) |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Less than 1,000 TPA |
INR 10,000.00 |
|
2 |
1,000 – 10,000 TPA |
INR 20,000.00 |
|
3 |
More than 10,000 TPA |
INR 50,000.00 |
B. EPR Registration Fees for Plastic Waste Processors (PWPs)
| Sr.No |
Production Capacity (TPA) |
Processing Fee (INR) |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Less than 200 TPA |
INR 5,000.00 |
|
2 |
200 – 2,000 TPA |
INR 20,000.00 |
|
3 |
More than 2,000 TPA |
INR 50,000.00 |
D. Annual Processing Charges
All registered PIBOs/PWPs must pay 25% of the initial application fee annually as the Annual Processing Fee.